Impact of Customer Journey Mapping on Customer Loyalty: The Mediated Moderated Model
Akash Khateeb1, Farhina Hameed2*, Malik Faiq Anjum3
Khateeb, A., Hameed, F., & Anjum, M. F. (2025). Impact of Customer Journey Mapping on Customer Loyalty: The Moderating Role of Customer Satisfaction. UW Journal of Management Sciences, 9(1).
ABSTRACT
Purpose: This study aims to investigate the relationship between Customer Journey Mapping (CJM) and Customer Loyalty (CL), examining the mediating role of Customer Experience (CX) and the moderating role of Customer Satisfaction (CS). While CJM is widely recognized as a tool for enhancing CX, its direct and indirect effects on customer loyalty remain underexplored. This research addresses this theoretical gap by analyzing how CJM practices influence customer loyalty and how customer satisfaction may strengthen this relationship. The study also contributes to the advancement of customer
relationship management (CRM) theories.
Design and Methodology: A mixed-method approach was employed, incorporating both qualitative and quantitative data. A structured questionnaire was administered to a sample of 357 customers in the textile sector, selected through stratified random sampling to ensure representative responses. Quantitative data were analyzed using descriptive and inferential statistics, with a 95% confidence level and a 5% margin of error. Qualitative data were gathered through customer feedback to provide deeper insights into customer perceptions of CJM and its implications. The study is grounded in Customer Experience
Theory and Relationship Marketing Theory, which form the theoretical foundation for the proposed research model.
Findings: The results confirm significant relationships between CJM, CX, CS, and CL. CJM has a direct positive effect on customer loyalty. Additionally, customer experience plays a mediating role, with better journey mapping leading to improved experience and, consequently, greater loyalty. Customer satisfaction further strengthens the link between CX and CL, serving as a key moderator in this dynamic. These findings highlight the interdependent nature of these constructs in fostering long-term customer relationships.
Implications: The research makes theoretical contributions through understanding how CJM affects loyalty through CX and CS. Practically, it suggests that organizations build CJM strategies that incorporate CX as well as measure customers’ satisfaction to make loyalty happen. Furthermore, this research advocates for an integrated approach to managing customer relationships in highly competitive environments and combines theory and practice to offer tangible implications for firms looking to improve retention and achieve sustainable growth. In highly competitive markets the long-term relationship with customers is managed through it.
Keywords: Customer Journey Mapping (CJM), Organizational Factors (OF), Customer Experience (CX), Customer Satisfaction (CS) & Loyalty (CL).
Introduction:
This research’s focus is on the lack of information on how Customer Journey Mapping (CJM) directly affects Customer Loyalty (CL) and the purposes of Customer Satisfaction (CS) and Customer Experience (CX) in this relationship. To develop the strategies organization faced problems not only to capture the intention of customers but also to retain customers over a long period of time (Ambrusevič, & Išoraitė, 2025). Basically, emerging customer journey mapping (CJM) plays an essential role in improving the customer’s experience (CX) and strengthening customer loyalty. For enhancing customers’ connections CJM directly and indirectly affects Customer Loyalty, and it remains untouched.
Although it is commonly acknowledged that CJM can be used to improve CX (Richardson, 2023; Padilla, Ascarza, & Netzer, 2024) there is not enough empirical data to show that CJM results in constant customer loyalty. Additionally, there is a substantial gap in literature due to the understudied mediatingrole of CX and the moderating effect of CS in this relationship. For companies looking to gain a competitive edge and create enduring customer relationships it is essential to comprehend how CJM CX CS and CL interact. Customer loyalty is a crucial factor in determining profitability and long-term success in the aggressively competitive market of today (Homburg et al., 2021).
However, organizations risk misallocating resources or failing to optimize their customer relationship strategies if they do not have a clear understanding of how CJM affects loyalty through CX and CS. By offering practical advice on how companies can use CJM to boost CX advance CS and eventually promote CL this study fills this knowledge gap. CJM is a useful tool for determining customer pain points and enhancing CX according to existing research (Richardson 2023; Padilla, Ascarza, & Netzer, 2024). Additionally, research has shown how crucial CX is as a mediator between different
business practices and CL (Lemon and Verhoef 2020; Homburg et al., 2021). Furthermore, it has been acknowledged that CS plays a crucial role in determining how CX and CL interact (Anderson & Sullivan, 2021). Yet there is a knowledge gap regarding how CJM CX and CS work together to influence CL because these studies have mostly concentrated on individual elements rather than how they are related. There are still a few gaps in the literature on CJM CX and CL despite their increasing amount. First there is little empirical data regarding CJMs direct effect on CL. Second, there hasn’t been enough research done on CXs mediating function in the CJM-CL relationship. Third, not enough research has been done on the moderating role of CS in the CX-CL relationship. In conclusion the generalizability of current findings is limited by the dearth of cross-industry and cross-cultural studies that validate these relationships.
This study integrates CJM, CX, CS and CL into a coherent framework which advances theoretical understanding of customer relationship management for academic research. By offering solid proof to back up current theories it also addresses the dearth of empirical research in this field. The results provide practitioners with practical suggestions for improving CX tracking CS and refining CJM tactics to cultivate enduring client loyalty. By stressing how these elements are interrelated the study offers a road map for companies looking to efficiently allocate resources and gain a sustained competitive edge. This study integrates recent research on CJM and CX (Homburg & Tischer, 2023) work on the changing role of CX in customer loyalty to reinforce the theoretical underpinnings. regarding how CX mediates business practices. The study also incorporates recent findings from Padilla, Ascarza, and Netzer (2024) expands upon Homburg et al., (2017) seminal work on CS and its effect on loyalty.
This study is important because it has the potential to close the gap between theory and practice. The study gives businesses the means to improve customer satisfaction and retention by offering a thorough grasp of how CJM CX and CS work together to affect CL. McLean & Wilson (2021), Additionally it advances future research in this area by extending and validating current theories which adds to the scholarly conversation.
Loyalty is the key to long-term success in the current dynamic business world and hence the concept of customer loyalty has gained critical importance. Customer loyalty could be used to describe the propensity of a customer creating repeated patronage of a brand or company and is impacted by the application of CJM together with the quality of the CX (Lemon & Verhoef, 2018). One of the fundamental approaches to managing customer journeys is CJM, a strategic process that
comprehensively maps and redesigns each successive contact the customer has with a brand with the goal of smoothing out the interactions and amplifying positive ones while minimizing the negatives (Kuehnl, Jozic, & Homburg, 2017). Customer experience has thus been recognized as a pertinent measure of customer retention. Based on literature, a customer’s experience that has been emerged by the C-Journey maps, generally boosts customer’s satisfaction and loyalty (Lemon & Verhoef, 2022). In this sense, the CJM promises successful experiences of different manifestations with the brand and an
understanding of the customer needs that allows addressing them accordingly. However, the part of the customer satisfaction as the moderating factor is worth mentioning while increasing its role in this process is being noticed. A positive customer experience which is a measure of the willingness of customers to continue buying a firm’s products or use its services due to their satisfaction, multiplies the overall impact of the customer satisfaction standards (Rosenbaum et al.,
2017). He further asserts that satisfied customers are likely to display superior loyalty and that thus, it is prudent that both customer journey mapping and experience be integrated within loyalty plans (Stickdorn, & Schneider, 2018).
This study will seek to understand customer journey mapping as an antecedent of customer loyalty, while engaging in the moderating variable of customer satisfaction, and the mediating variable of customer experience. Combining these variables will assist the study in offering a more elaborate explanation of how various strategic CJM initiatives can increase customer loyalty by providing them with better experiences, especially in contexts that boast high levels of satisfaction among customers.
1.1 Research Problem:
Most of the essential studies contributed that Customers Experience CX improves Loyalty, so there is a lack of empirical evidence explaining how CJM directly and indirectly specifically affects loyalty Stein and Ramaseshan (2020). Moreover, academic attention on the moderating role of customer satisfaction CS in this dynamic relationship is inadequate. the insufficient knowledge of these interrelations, organizations risk not overcome, CJM fully focused to maintain potential to drive Loyalty Abrar et al. (2020).The objectives of this study are threefold: first, to investigate the direct relationship between Customer Journey Mapping (CJM) and its impact on Customer Loyalty (CL); second, to examine the mediating role of Customer Experience (CX) in the relationship between CJM and CL; and third, to explore whether Customer Satisfaction (CS) moderates the relationship between CX and CL.
The theoretical contribution of the study is the investigation of customer journey mapping and customer loyalty (Howard & Lee, 2019). The study adds knowledge in the body of literature by measuring the mediating and moderation effect. For sustaining profitability and achieving competitive advantage Customer loyalty plays a vital role. Therefore, researchers and practitioners have complete knowledge of mechanisms by which CJM influences loyalty. Specifically, industries like retail and clothing significantly affect their business where shifts to competitors are easy and switching costs are low. By identifying customers’ pain points, customers’ experience is enhanced through CJM that helps better understand the literature (Abrar et al., 2020). Satisfaction and loyalty increased by the positive outcomes of customer experience CX. isolated relationships have focused most of the studies rather than offering a holistic framework connecting CJM, CX, CS, CL. There is sufficient research to examine CJM on CL to have direct influence. Customers experience CX have a meditating role in the relationship between CJM and CL. and the moderating role of Customer satisfaction between CJM and CL.
Moreover, there is a lack of empirical validation between cultural contexts and industry sectors (Nobar & Rostemzadeh, 2018).
For managerial touchpoint, this study helps businesses to increase customer loyalty through effective customer journey mapping. By finding the pain points through customer journey and improving the customer experience and ultimately expanding loyalty and satisfaction. Low switching cost and intense competition the businesses need to differentiate their product by better understanding of CJM, CX and CS to retain the customers as well and increase market share.
2. Literature Review
CJM is a tool of strategic management that shows customers experience interactions with brands which visually represent the sequence. Ambrusevič, & Išoraitė, (2025) explains, for optimizing the customers touchpoints, and designing better experience CJM helpful for organization to identify pain points (Richardson, 2010). There will also be a literature review of the extant literature on customer journey mapping literature and literature on customer loyalty. In this modern business world where competition is tight, it has become very important for organizations to attain and sustain their customers’ loyalty (Khan, 2024). When the expectations of a customer are met or exceeded by a product or service, this is what is referred to as customer satisfaction, which has a direct impact on the level of loyalty that a business will experience or the potential revenue it will garner in the long run (Anderson & Sullivan, 2020). Happy customers are likely to repurchase, refer to other consumers to the company brands, and encourage others to engage in further buying within the company’s favor, thus leading to competitive supremacy (Jones & Sasser, 2019).
2.1 Customer Journey Mapping and Customer Satisfaction
Customer journey mapping is a strategic management tool that can be considered as essential by the practitioners and discussed in academic literature because of the tool’s importance in identifying an organization’s customer loyalty (Anderson & Sullivan, 2020; Jones & Sasser, 2019). This can be useful to an organization’s strategic management team in a way that helps it Darw incites which touch points are strategic to customer retention. It can also identify strategic actions in respect to each touchpoint, leading to a multi-disciplinary approach on organizational service and product development enhancement (Hamilton et al., 2021; Klein et al., 2020; Rosenbaum et al., 2017). Furthermore, Akter et al. (2019) have suggested that the overall idea of CCM should be complimented by the understanding that customer journey innovativeness is one of the factors that needs to be scrutinized for successful firm innovation, as customers evaluate various firm activities before forming their overall assessment of its innovativeness (Hamilton et al., 2021; Kunz et al., 2018). Customer journey mapping can result in the elimination or minimization of pitfalls, and hence, create a far more satisfying journey for the customers (Lemon & Verhoef, 2016). This proactive approach brings in its wake a reduction in the number of frustrating incidents that a customer may come across hence there is a boost in loyalty (Rosenbaum et al., 2017). Graphically framing the existence of all customer phases helps to redesign service processes to be closer to the customer. This can lead to an accumulation of efficiency in the provision of services delivery and satisfaction from the side of the customers because they are offered services of high quality and standard as expected.
2.2 Customer Journey Mapping & Customer Experience
Customer journey mapping ‘maps’ the customer’s interaction with a brand or company and is one of the most effective methods of mapping the processes that occur during the consumption process (Hamilton et al., 2021; Lemon & Verhoef, 2019). This strategy is very important especially in the improvement of the CX model which intends to depict all the views and emotions that the customer may have regarding a certain brand based on all the exchange activities that have been done before (Khan, 2018). When design thinking is applied to map out the customer’s journey, this makes it easier to devise
ways of improving CX since the behaviors, requirements as well as the problems that customers are likely to have, are well understood (Olabode, 2024). Customer Journey Mapping is an effective tool that designs the process of customers’ interactions starting from the stage when they pay attention to a company and till the time, they have ended any relationship with a particular company (Rosenbaum et al., 2017). This approach is crucial in defining customer journey mapping since it allows for understanding sources that affect the notion and define its key points.
Customer Experience Theory, as put forward by Lemon & Verhoef in their article on Customer Experience, suggests that all the touch-points have an assimilated effect on the overall experience and the resultant level of customer satisfaction, which will define his/her loyalty (Okeke et al., 2024). Customer touch points are one of the important concepts of approving the interaction points of a customer with the brand and its relevant business unit. Such an alignment allows organizations to guarantee that each of the defined touch points is effectively and sustainably geared to consumer desires, encouraging
an improved experience.
2.3 Customer Experience and Customer Loyalty
Customer loyalty has certain parameters that are of immense importance to business ventures that want to achieve sustainable performance. Customer experience (CX) is a critical factor and a specific means by which firms gain such outcomes. In this literature review, customer satisfaction, customer loyalty and customer experience are explored and how a good customer’s experience will in turn enhance the level of satisfaction and loyalty that a customer will express towards the firm (Kumar et al., 2021).
CX Theory further argues that the total of these individual interactions with the organizational member determines the consumer’s overall experience (Pansari & Kumar, 2017). The overall impression derived from all or some of these contact points enhances satisfaction and loyalty levels among customers (Lemon & Verhoef, 2021).
Over the years, academic research has provided evidence that better quality of customer experience equates to a higher satisfaction level. Benedettini (2024) observed that the satisfaction level of consumers is highly dependent on interactions perceived at the service contact points. The perceptual consumer experience enhances the probability of the achievement of the agreed-upon objectives due to the positive association that comes with satisfaction (Homburg et al., 2017).
The analysis of the customer journey shows where touchpoints are most important to the customer and therefore influences the buying process. Through optimizing these interaction points, one is able to increase the level of loyalty and satisfaction (Richardson, 2010). Higher levels of customer engagement can also be achieved by using the information acquired from customer experience subsequently to customize communications with the customers, which in turn results in customers’ satisfaction and increased commitment (Rawson et al., 2013).
2.4 Customer Journey Mapping and Customer Loyalty
Customer journey map (CJM) is a framework through which the totality of a customer or consumer is depicted concerning their experiences within an organization or business (Padilla, Ascarza, & Netzer, 2024). CJM helps in understanding the major concerns in the customer journey map and such vital aspects as customer dissatisfaction points and growth areas (Richardson, 2010). There is little doubt that by mapping out the continuum of the customer relationships at each point of successful or potential breakdown in the relationship it will be easier to tell where and CJM has been found to facilitate constant delivery of the business’s messaging to customers throughout their interactions with the business to earn their satisfaction (Rosenbaum et al., 2017). As the consumers engage with a particular brand, make a cumulative of several experiences, they can perceive they have had a satisfying experience. Customer journey mapping helps in matching the customer’s perception of what it is going to be, and what he in fact is given or experienced thus minimizing the chance of disappointment (Lemon & Verhoef, 2021).
From awareness to post-purchase evaluation, companies need to manage customers’ expectations so that the experiences they offer are positively aligned with customers’ perception, hence leading to high satisfaction levels. Through the above propositions, CJM helps business organizations to address the needs and satisfactions of diverse customer segments in their own unique ways (Lemon & Verhoef, 2021). Cognitive maps can help companies identify the different paths customers may travel through the business ecosystem and the different points of contact that they have along the way; through better understanding of such paths and points of contact, companies can tailor the customers’ experience and offer, ultimately achieving higher satisfaction levels. It indicates that the customer journey maps are open to learning, and hence customers’ satisfaction could be improved as the organizations strive to optimize
the journey maps (Rosenbaum et al., 2017). As a live tool, CJM is well-suited to support and manage customer satisfaction as a strategic goal during the whole customer life cycle. The different types of research show that customer journey mapping is a key factor in enhancing customer satisfaction through the identification of the customer pains, gaps and constraints, mapping and creating coherence to the touch points or interaction points, managing expectations, customizing the customer experience as well as continuously improving the interaction journey with the firm (Lemon & Verhoef, 2021).
Theoretical Framework:
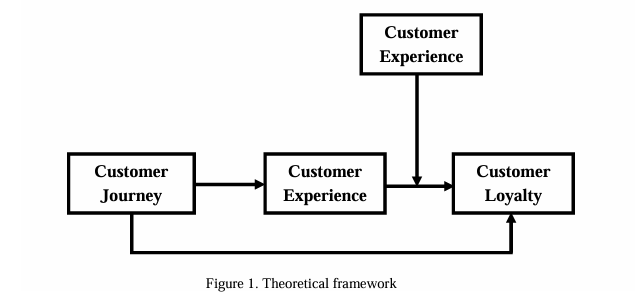
2.5.1 Customer Experience (CX) Theory
Customer experience theory (CX) contributes and shapes every touch point as well as interaction of customers with brands across various channels. Customers’ overall perception is influenced by each touch point and significantly affects satisfaction and loyalty, so that’s why CJM helps to optimize touch points. Due to well-mapped journeys the emotional bonds become stronger and enhance loyalty. The relationship between customer journey mapping and customer loyalty is better mediated by customer experience. Customer Experience (CX) Theory refers to the situation of recognizing all the activities the customer goes through within his or her dealings with a specific brand starting from the earliest stages to after buying a product from that brand. According to this theory, every single point of contact that the customer has with the organization adds to the valuation of the brand, thus affecting the level of customer loyalty (Lemon & Verhoef, 2016). CX theory, in the process of the customer journey map, points out how the process assists businesses in explaining the grand cultural touch points that define its customers’ experience (Rosenbaum et al., 2017). It notes that organizations should strive to manage and enhance these contact points so that consumers receive a better and more fulfilling experience; one outcome is higher satisfaction levels and customer loyalty. Improving Touch points With the help of customer journey maps one sees that there are some certain points as to how communication with the customer may be altered in order to raise generally the level of their satisfaction (Lemon & Verhoef, 2016). Holistic View Customer journey mapping gives a wider emphasis on the different customer touch points with the brand to enable organizational processes to be realigned to the customers’ wants and increase customer satisfaction (Richardson, 2010). It enables measuring and analyses many different aspects of the client experience and prevents areas of dissatisfaction before the customer is affected (Rosenbaum et al., 2017).
2.5.2 Relationship Marketing Theory
CJM ensured that every touch point strengthened trust and satisfaction of customers in this research. The relationship between customer experience and customer loyalty is moderate by customer satisfaction which enhances the positive relationship. Thus, relationship marketing theory integration verifies the moderating effects of Customer satisfaction and also better understanding of customer loyalty results mapping the customer journey efforts.
The theoretical framework for Relationship Marketing Theory is based on the notion that marketing efforts are geared toward the establishment and continuing maintenance of relationships with customers rather than the formation of a single transaction. The customer equity model posits that long lasting focused positive touch points result in customer acquisition, while high-quality touch points result in customer retention (Reinartz, & Kumar, 2003). Relationship Marketing Theory supports the CCM by emphasizing that value exchange throughout the touch points of the customer journey needs to be consistent to enhance customer relationships. Analyzing the ‘customer touch points,’ it’s easy to evaluate
customer needs and subsequently, tailor positive effort to ensure customer loyalty. Since all the points of interacting with customers create a positive image, customer journey mapping is useful in customer development, since it helps in delivering all the touch points to meet or even exceed the expectations of the customers (Morgan & Hunt, 2012). Customer journey mapping focuses on the importance of creating a coherent pattern of customer interactions because each contact point can have significant impact on constructing long-term and stable business relationships (Gronroos, 2017). By enabling a good customer experience, a firm builds customer affection and loyalty, which is beneficial for positive word-of-mouth recommendations (Reinartz & Kumar, 2019).
2.6 Hypotheses
H1: Customer journey mapping is positively related to customer loyalty
A strategic tool called customer journey mapping (CJM) assists companies in visualizing and comprehending the actions that consumers take when interacting with a brand. CJM improves the overall customer experience by pinpointing problems and streamlining touch points. Increased convenience tailored interactions and smooth service delivery are all results of a well-designed customer journey, and these factors ultimately increase customer loyalty and trust (Homburg et al., 2017). Through boosting positive word-of-mouth recommendations, decreasing churn and promoting repeat business, this improved engagement helps to foster customer loyalty. Therefore, it stands to reason that customer loyalty and effective CJM are positively correlated.
H2: Customer experience mediates the relationship between customer journey mapping and customer loyalty.
One important element influencing consumer attitudes and behavior is customer experience (CX).
Through better service design, less friction in interactions and maintaining consistency across channels CJM has a direct impact on CX. Higher satisfaction and enduring loyalty result from a satisfying customer experience that is molded by an efficient journey map and fortifies the emotional bond between the consumer and the brand (Rosenbaum et al., 2017). Consequently, CX serves as a mediator in this relationship indicating that CJMs effect on customer loyalty is achieved through improving the customer experience. H3: Customer satisfaction moderates the relationship between customer experience and customer loyalty, such that the relationship is stronger when customer satisfaction is high. A key determinant of the strength of the correlation between CX and customer loyalty is customer satisfaction (CS). Although a satisfying customer experience helps foster loyalty its impact is amplified when customers are extremely happy. A high degree of satisfaction indicates that consumers believe the brand meets or surpasses their expectations. This strengthens the customers’ emotional bond with the brand increasing the likelihood that they will stick with it, refer it to others and stay involved over time. On the other hand, even a satisfying experience might not be sufficient to win over a customer’s loyalty over the long run if they are not satisfied (Lemon & Verhoef, 2016). The relationship between CX and customer loyalty is therefore moderated by customer satisfaction. The impact of CX on loyalty increases with the level of satisfaction.
3. Methodology
3.1 Purpose of the Study
Examining the relation between customer journey mapping, customer experience and customer satisfaction in shaping customer loyalty is the primary focus or purpose of the study. Interaction between these variables is investigated in this study. The aim of this research is to examine how businesses improve consumer loyalty while improving customer journey mapping as well as customer experience and enhance the business productivity.
3.2 Population and Sampling
The population for a study investigating the impact of customer journey mapping on customer satisfaction and loyalty typically consists of two main groups: The customers who interact with the company’s products or services and have experienced various touch points of the customer journey. This group can be segmented based on demographic factors (age, gender, income), psychographic factors (lifestyle, values), behavioral factors (purchase history, brand loyalty), and geographic factors (location). Understanding the customer perspective is crucial because the primary goal of customer journey mapping is to enhance their satisfaction and loyalty. Collecting data from customers helps identify which touch points are most impactful and where improvements are needed.
3.3 Sample Size
The sample size for a study on the impact of customer journey mapping on customer loyalty with the moderating role of customer satisfaction is determined based on statistical principles and practical considerations. For a robust quantitative analysis, aiming for a sample size of approximately 380 customers of a clothing business, 400 questionnaires were distributed, but 357 responses were collected, which was appropriate to work, and it would provide reliable results with a 95% confidence level and a 5% margin of error. The same 357 responses were analyzed, focusing on customers’ perceptions of their experiences across different touch points.
3.4 Sampling Technique
Stratified Random Sampling is often the best choice for this type of study because it ensures that key subgroups (e.g., different industries, company sizes, customer demographics) are adequately represented. This technique enhances the precision and generalizability of the findings. Businesses determine the relevant strata such as industry type and company size. customers collect data based on age, gender and purchasing behavior. Create distinct groups Based on identified subgroups. Calculate the proportionate sample size needed from each stratum to reflect its size in the overall population. Use a random selection method to choose participants within each stratum. For a study investigating the impact of customer journey mapping on customer satisfaction and loyalty, stratified random sampling is recommended due to its ability to ensure that diverse and key subgroups are well-represented, thereby enhancing the robustness and generalizability of the study results.
3.5 Unit of Analysis
Individual consumers are the unit of analysis for this research. The respondents are the shoppers.
3.6 Data Collection Procedure
Quantitative data will be gathered through structured surveys distributed. Data was collected through structured surveys distributed both in physical stores and online platforms, ensuring diverse representation of customer experiences. A mix of quantitative survey questions and qualitative feedback was collected to assess customer experience. A Likert scale (1-5) measured satisfaction levels, categorizing customers into low, moderate, and high satisfaction groups. Each item would be measured on the five-point Likert scale ranges from strongly disagree to strongly agree. The numbers of the scale can be defined as the “1” represents “Strongly disagree”, “2” denotes “Disagree”, “3” denotes “neutral”, “4” denotes “agree”, “5” denotes “strongly agree”
3.7 Time Horizon
Cross sectional design has been used in this study with a data collection of one time that comprised of 15 days.
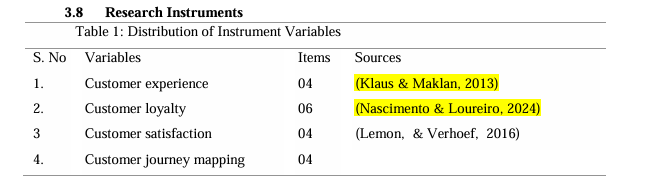
Klaus, P. P., & Maklan, S. (2013). Towards a better measure of customer experience. International journal of market research, 55(2), 227-246. http://dx.doi.org/10.2501/IJMR-2013-021
4. Data Analysis
This chapter summarizes the results of descriptive statistics, hypothesis testing, data collection analysis and correlation analysis. The design of questionnaires has two main sections. The first section consists of questions related to the demography of the respondents such as age, gender and education level. The second section consists of questions related to dependent variables i.e. customer loyalty, meditating variables i.e. customer experience and independent variables i.e. customer journey mapping and moderator customer satisfaction.
4.4 Demographic Analysis
The sample were 60% females and 40% males. 52% made in-store purchases and 48% made online purchases. The most common departments represented are Customer Service (48%), Marketing (44%), and IT (08%).

Reliability Cronbach’s alpha: Measures the internal consistency of the items measuring each construct. Values above 0.7 are considered acceptable. Validity Convergent validity: Measures whether items that are supposed to be related are related. Average variance extracted (AVE) values above 0.5 indicate acceptable convergent validity. Discriminant validity measures whether constructs that are supposed to be unrelated are actually unrelated. The square root of the AVE for each construct should be greater than its correlations with other constructs. For this paper values are in range.
4.6 Normality Statistics
To assess whether the data is normally distributed, the following statistics can be calculated. Skewness Measures the symmetry of the distribution. Values between -1 and 1 are considered acceptable. Kurtosis Measures the peaked Ness of the distribution. Values between -3 and 3 are considered acceptable. Shapiro-Wilk test Tests the null hypothesis that the data comes from a normally distributed population. A p-value greater than 0.05 indicates the data is normally distributed. For this paper data is normally distributed.
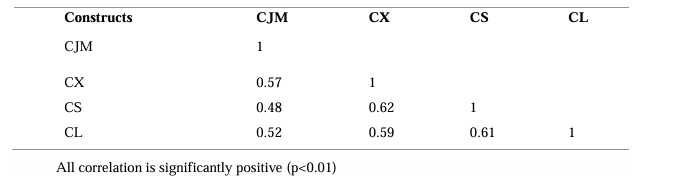
4.7 Correlation Analysis
Pearson correlation coefficients can be calculated to measure the strength and direction of the relationships between the variables. Values range from -1 to 1, with -1 indicating a perfect negative correlation, 0 indicating no correlation, and 1 indicating a perfect positive correlation.
Table 5: correlation analysis
4.8 Hypothesis Testing
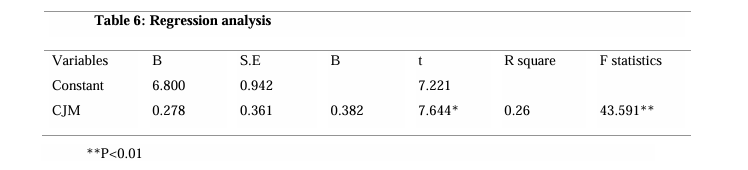
To test the hypotheses a regression analysis is conducted. Table 6 shows the significant direct effect of CJM on CL.
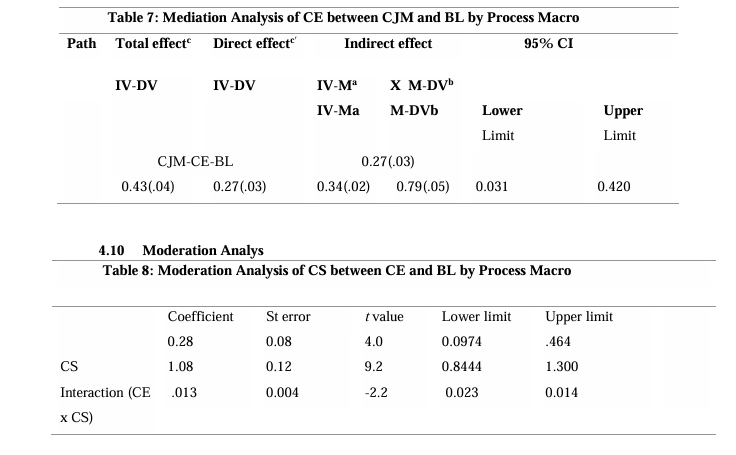
4.9 Mediation Analysis
A path analysis was conducted to test the mediating effect of CE between CJM and BL. Results shown in Table are based upon 5000 bootstrapped samples indicating that total effect (.43, p<.05) and indirect effect (.27, p<.05) is significant. The results indicate that CE mediates the relationship between CJM and BL (lower 95% CI = .031 and upper 95% CI= .420). The direct effect (.27, p<.05) is also significant thus, shows partial mediation exists (Chang et al., 2013).
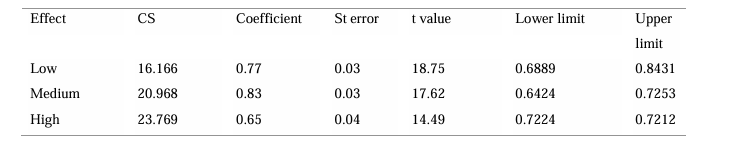
To test Hayes & Preacher (2014) (Model 1)’s moderation study of CS between CE and BL via Process Macro, a route analysis was performed. First, the significance of the moderation effect is determined; if it is significant, then moderation exists and is meaningful, as evidenced by the values of the lower and upper limit confidence intervals. When zero does not fall between the two extremes, moderation is significant. The fact that the lower limit is 0.23 and the higher limit is 0.014 indicates that zero does not lie between the two values, indicating that moderation exists. Table 8 demonstrates the low, medium, and high effect of SI in the relationship between ATML and BITML to determine which condition has a significant effect.
Discussion and Conclusion
The findings of this result show that CJM has a complex relationship between customer experience, customer satisfaction and customer loyalty. Customer journey mapping has a positively significant impact on customer loyalty (CL). Richardson (2010) theoretical proposition supported by these results as well as Rosenbaum et al,. (2017) and Johnson & Mathews, (2021) evidence proved empirically, who contributed that Customer journey mapping improves perception, trust and loyalty of the customer. These insights strengthen our study that customer journey mapping enhances customer loyalty. Customer journey mapping also has significant impact on customer experience, the strategic goal of the companies is to design and create the best customer journey approach and for this they are focusing on creating an effective customer experience at all touch points (Halvorsrud et al., 2024). The study’s conclusions significantly advance our knowledge of the interdependencies between customer satisfaction (CS), customer loyalty (CL) customer experience (CX) and customer journey mapping (CJM). These results provide theoretical and practical insights while also complementing and enhancing the body of existing literature. To support the necessity of this research we go into further detail below about how the study’s conclusions connect to and expand upon current academic work Lemon and Verhoef (2016). The research verifies that CJM has a significant and positive impact on customer loyalty. The study confirms that CJM directly improves CL which is in line with Lemon and Verhoef’s (2016) findings that improve customer satisfaction and loyalty by optimizing customer touch points through CJM. By outlining and refining every phase of the customer journey businesses can establish smooth effective procedures that satisfy clients and promote loyalty. This supports the claim made by Rosenbaum et al., (2017) that CJM aids in identifying problems and areas for development which eventually results in improved customer relations. Although these studies emphasize the significance of CJM there is little empirical data regarding the direct effects of CJM on CL especially in a variety of cultural and industrial contexts. In order to fill this knowledge gap, the current study offers solid proof of the beneficial correlation between CJM and CL which advances our theoretical knowledge of CJMs function in customer relationship management. The study supports the findings of Homburg et al., (2017) who contend that CX acts as a link between loyalty and business practices by confirming that CX mediates the relationship between CJM and CL. This shows that CJM is not only sufficient customer experience but also emphasizes and enhances the loyalty outcomes.
The mediation effect emphasizes that although CJM establishes the groundwork for better customer interactions, better CX is how these initiatives are converted into devoted behaviors. This is consistent with the findings of Lemon and Verhoef (2021) who stress that the cumulative impact of all touch point’s shapes CX and that CJM offers a comprehensive perspective on these interactions. Notwithstanding these realizations there isn’t a thorough analysis of how CJM affects CX and CL in literature. This study closes this knowledge gap by examining the mediating function of CX empirically which helps to clarify the ways in which CJM promotes loyalty. The study’s finding that CS plays a moderating role in the relationship between CX and CL is consistent with Anderson and Sullivans (2020) contention that satisfaction increases the influence of positive experiences on loyalty. The findings demonstrate that a strong relationship between CX and CL results in more repurchases and favorable word-of-mouth when customers are extremely satisfied. This supports the assertion made by Kumar and Pansari and Kumar (2017) that CS is a key factor in fostering enduring loyalty. However, the literature has not fully examined CSs moderating function in relation to CJM and CX. This study fills this knowledge gap by showing how CS improves CJM and CXs ability to foster loyalty providing insightful information for practitioners and scholars alike.
Filling in gaps in literature, the study’s findings advance theoretical understanding of how CJM CX CS and CL are interconnected. For example, Padilla, Ascarza, and Netzer (2024) emphasize that more empirical research is needed to fully understand how CJM affects loyalty while Lemon and Verhoef (2021) demand a more thorough examination of the mediating and moderating factors in this relationship.
By filling in these gaps the study offers a more thorough framework for comprehending how CJM can be used to improve loyalty. Practically speaking, the findings provide organizations with doable suggestions (Homburg, & Tischer 2023). The significance of employing CJM to maximize digital touch points for instance is emphasized by McLean and Wilson (2021) whereas Kumar et al. (2021) emphasize how customized experiences affect customer loyalty. To promote long-term loyalty, the current study expands on these insights by showing how businesses can use CJM to enhance CX and CS. From these findings, the state of the art for this study offers significant understanding of the existence of the relationship among CJM, CX, Customer satisfaction, and Customer Loyalty. In this section, the author shall present a synthesis of the main ideas as well as the relevant implications. The study also validates the measures of customer loyalty which reveals that CJM has a positive influence on the subject (Lemon & Verhoef 2016). Through the proper mapping and improvement of the different stages that a customer goes through during his/her interaction with a business, the flow of the process can be made more efficient and thus the general satisfaction of the customer improved, hence creating loyal customers. This identifies further that it is crucial for organizations to invest in CJM initiatives as these initiatives aim to foster long-term customer relationships. With regards to the research hypotheses, customer experience was also observed to moderate between CJM and customer loyalty. This goes further to mean that any gains made in the CX process through powerful CJM would translate to a higher level of customer loyalty. Customer journey mapping lay the initiative groundwork suggested by the mediated role of customer experience CX. The quality of customer experience increases the customer loyalty, it is through CX where these are rewarded with loyal behaviors. Hence, it may be concluded that, for CJM to deliver benefits at their fullest, organizations need to prioritize the CX improvement across each of the touch points (Homburg et al., 2017).
5.1 Conclusion
All things considered, this study adds to and expands upon the body of literature by presenting empirical data supporting the connections between CJM CX CS and CL. By filling in the gaps in literature and relating the results to current research the study provides insightful theoretical and practical information. In addition to offering practical suggestions for businesses looking to maximize their customer relationship management strategies it proves that CJM is a successful strategy for improving CX and CS which in turn fosters loyalty. In addition to adding to the body of knowledge in academia regarding customer relationship management this research provides useful resources that help companies gain a sustained competitive edge. Furthermore, the present research aims to test the influence of CJM on customer loyalty, where the moderating role of customer satisfaction and mediating role of customer experience will also be examined. The results further all emphasize that optimal CJM has positive effects on customer loyalty in that it positively impacts CX at multiple points. Furthermore, the positive interaction between CX and loyalty is further enhanced if the process is supported by customer satisfaction, which underscores the important role of this factor. From such findings, it is feasible to argue that organizations are receptive to substantial customer loyalty through CJM strategies that further CX and continually remodel customer value expectations. The research contributes to the theoretical body of knowledge of those relationships and phenomena and provides practical guidance for enhancing organizational customer loyalty based on the typology of journey maps and experience management efforts.
5.2 Implications
The extent to which customers are satisfied with the CX delivered was cited as another independent predictor of a strong bond between CX and customers’ loyalty. Loyalty increases with a good CX and this is even more so when customers are satisfied. Hence, while enhancing CX is central to the management and achieving organizational goals, it is equally important that the experiences should be optimally delivered as per the customer’s expectations. Since repurchasing is a sign of satisfaction, there is a great deal to be gained by organizations interested in customer satisfaction that have got to monitor and improve their customer satisfaction scores. Indeed, the research evidence presented in this study shows that CJM, CX, customer satisfaction, and loyalty are related and interdependent factors. By enhancing the features of the organization to improve or optimize CJM, customer experience is alleviated, thus increasing customer satisfaction, loyalty included (Pansari & Kumar, 2017). This system of connections implies that organizations should implement a CJM process alongside ongoing activities to enhance the general CX, while tracking the levels of satisfaction among clients. To the practitioners, the results offer practical means of informing resource distribution. CJM is something businesses need to consider as a strategic focus for enhancing the CX as well as increasing customer retention. Firms should examine regularly the satisfaction to strengthen the positive relationship experience on loyalty. In a dynamic market, competitive advantage creates tools monitoring by integrating the journey mapping with customer satisfaction.
In the same circumstances, they should also adopt provisions for assessing customers’ satisfaction levels to discover other grounds for improvement. The research also fills the theoretical gap as to the roles and interdependencies of the CJM, CX, customer satisfaction, and loyalty. This is helpful in expanding the existing theories and propose more solid evidence on the way that businesses can work on customer relationships from the aspect of management (Rosenbaum et al., 2017). In sum, the research shows that CJM is an effective approach to increase customer loyalty and to build a sustainably strong relationship between the companies and their clients, which is amplified when combined with the strategies aimed at increasing CX and keeping high levels of customers’ satisfaction. Studying the outlined findings can help enhance the methodological base of theoretical and empirical developments within the CRM field for academic research and provide practical recommendations for business applications.
5.3 Limitations
In the clothing sector the research was conducted solely. Generalizability of findings to other industries may be limited like Hospitality, banking etc. Future researchers examine the model in diverse sectors and expand the body of knowledge or applicability of the outcomes. Longitudinal studies are recommended to investigate the impact of Customer journey mapping on loyalty overtime. The sample size used in this study may limit the generalizability of the findings. If the sample is not large or diverse enough, the results may not accurately represent broader customer populations across different industries or regions. The study relies on self-reported data from surveys, which can introduce biases such as social desirability bias or recall bias. Respondents might overstate positive experiences or underreport negative ones, potentially skewing the results.
The study employs a cross-sectional design, capturing data at a single point in time. This limits the ability to infer causality or understand changes in customer behavior and satisfaction over time. Longitudinal studies would provide deeper insights into how CJM influences loyalty. The findings may be influenced by the specific industries or sectors examined in the study. Different industries may have unique customer journey characteristics, which means the results might not be applicable to all business contexts without adjustments. The measurement of complex constructs like customer experience, satisfaction, and loyalty might not fully capture their multifaceted nature. More nuanced measurement tools or mixed-method approaches could provide a richer understanding of these variables.
References
Abrar, K., Saeed, M. A., Ahmad, I., & Ali, S. (2020). How Customer Experience Quality affects Customer Satisfaction-Loyalty with Moderating role of Competitive Choices and Familiarity:
Assessment of Private Hospitals in Pakistan. Sukkur IBA Journal of Management and Business, 7(1), 75-91.
Ambrusevič, N., & Išoraitė, M. (2025). User experience journey map: theoretical and practical aspects. Journal of Entrepreneurship & Sustainability Issues, 12(3).
Anderson, E. W., & Sullivan, M. W. (2020). The antecedents and consequences of customer satisfaction for firms. Marketing Science, 12(2), 125-143.
Benedettini, O. (2024). Strategic emphasis, outsourcing intensity, and financial performance in digital servitization. Industrial Marketing Management, 122, 1-12. Chang, H. H., Jeng, D. J. F., & Hamid, M. R. A. (2013). Conceptualising consumers’ word-of-mouth behaviour intention: evidence from a university education services in Malaysia. Service
Business, 7, 17-35.
Choices and Familiarity: Assessment of Private Hospitals in Pakistan. Sukkur IBA Journal of Management and Business, 7(1), 75-91.
Grönroos, C. (2017). Service management and marketing: Managing the service profit logic (4th ed.). Wiley.
Homburg, C., & Tischer, M. (2023). Customer journey management capability in business-to-business markets: Its bright and dark sides and overall impact on firm performance. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 51(5), 1046-1074.
Halvorsrud, R., Kvale, K., & Følstad, A. (2024). Customer journey mapping: A review and research agenda. Journal of Service Theory and Practice, 34(1), 45–65.
Hamilton, K., Dunnett, S., & Piacentini, M. (2021). Consumer vulnerability, social power, and marketing ethics. Journal of Business Ethics, 152(2), 199–207.
Homburg, C., Jozić, D., & Kuehnl, C. (2017). Customer experience management: toward implementing an evolving marketing concept. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 45, 377-401.
Howard, M. C., & Lee, J. D. (2019). Journey mapping as a tool to improve the customer experience.
International Journal of Market Research, 61(2), 123-139.
Johnson, C., & Mathews, B. (2021). Customer journey mapping: Insights and best practices. Journal of Business Strategy, 42(1), 65-75.
Jones, T., & Sasser, W. (2019). Why satisfied customer’s defect. Harvard Business Review, 73(6), 88 99.
Johnson, C., & Mathews, B. P. (2021). Customer journey mapping: Best practices for understanding customers. Journal of Business Strategy, 42(1), 65–75.
Klein, J. F., Falk, T., Esch, F.-R., & Gloukhovtsev, A. (2020). Linking pop-up brand stores to brand experience and word of mouth: The role of perceived authenticity and experiential value. Journal of Business Research, 113, 29–37.
Khan, Z. (2024). How Customer Loyalty and Satisfaction Influences Strategic Market Management: A
Literature Survey. Sustainable Business Management Review, 1(2), 49-54.
Kumar, V., Pansari, A., & Rajan, B. (2021). Customer engagement: Concept, implications, and future research directions. Journal of Service Research, 24(1), 3–18.
Kunz, W., Hogreve, J., Rajab, T., & Eggert, A. (2018). Customer engagement in a Big Data world. Journal of Service Management, 29(5), 718–739.
Lemon, K. N., & Verhoef, P. C. (2016). Understanding customer experience throughout the customer journey. Journal of Marketing, 80(6), 69-96.
Lee, Y., & Kozar, K. A. (2022). Customer journey mapping: Case studies and applications. International Journal of Information Management, 58, 102315.
McLean, G., & Wilson, A. (2021). Shopping in the digital world: Examining customer engagement through augmented reality mobile applications. Computers in Human Behavior, 116, 106597.
Mandic, I. (2024). Enhancing customer journey through process mining: A literature review and future research directions. In Proceedings of the First International Conference FUTURE-BME 2024: Forging the Future – Pioneering Approaches in Business and Management (p. 987). Morgan, R. M., & Hunt, S. D. (1994). The commitment-trust theory of relationship marketing. Journal of Marketing, 58(3), 20–38.
Nascimento, J., & Loureiro, S. M. C. (2024). Mapping the sustainability branding field: emerging trends and future directions. Journal of Product & Brand Management, 33(2), 234-257.
Nobar, H. B. K., & Rostamzadeh, R. (2018). The impact of customer satisfaction, customer experience and customer loyalty on brand power: empirical evidence from the hotel industry. Journal of Business Economics and Management, 19(2), 417-430.
Okeke, N. I., Alabi, O. A., Igwe, A. N., Ofodile, O. C., & Ewim, C. P. M. (2024). Personalized customer journeys for underserved communities: Tailoring solutions to address unique needs. World Journal of Advanced Research https://doi.org/10.30574/wjarr.2024.24.1.3205 and Reviews, 24(1), 1988–2003.
Olabode, S. O. (2024). An Empirical Study On The Impact Of Effective Digital Customer Journey
Management On Customer Satisfaction In The Nigerian Islamic Banking Sector (Doctoral dissertation, Doctoral dissertation, University of Bolton).
Padilla, N., Ascarza, E., & Netzer, O. (2024). The customer journey as a source of information. Quantitative Marketing and Economics, 1–40. Pansari, A., & Kumar, V. (2017). Customer engagement: the construct, antecedents, and consequences. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 45, 294-311.
Rawson, A., Duncan, E., & Jones, C. (2013). The truth about customer experience. Harvard Business Review, 91(9), 90–98.
Reinartz, W. J., & Kumar, V. (2003). The impact of customer relationship characteristics on profitable lifetime duration. Journal of Marketing, 67(1), 77–99.
Richardson, W. (2010). Blogs, wikis, podcasts, and other powerful web tools for classrooms. Corwin press.
Rosenbaum, M. S., Otalora, M. L., & Ramírez, G. C. (2017). How to create a realistic customer journey map. Business Horizons, 60(1), 143-150.
Stein, A., & Ramaseshan, B. (2020). The customer experience–loyalty link: moderating role of motivation orientation. Journal of Service Management, 31(1), 51-78.
Stickdorn, M., Hormess, M. E., Lawrence, A., & Schneider, J. (2018). This is service design doing. ” O’Reilly Media, Inc.”.
Witell, L., Kowalkowski, C., Perks, H., Raddats, C., Schwabe, M., Benedettini, O., & Burton, J. (2020).
Characterizing customer experience management in business markets. Journal of Business Research, 116, 420-430.
